Free Ship Over $75
15% OFF First Order
-
Shop
NEW & NEATURED
SHOP BY HEALTH BENEFITS
-
About Us
-
Shop
NEW & NEATURED
SHOP BY HEALTH BENEFITS

-
About Us
Free Ship Over $75
15% OFF First Order


In pharmaceutical formulations, certain drugs, such as poorly soluble drugs, low-melting-point substances, highly potent compounds, and moisture- or heat-sensitive medications, often present significant challenges in traditional oral solid dosage forms like tablets and standard hard capsules. These challenges include complex manufacturing processes and unstable product quality. With the advancement of formulation technologies and equipment, a novel dosage form has emerged: the liquid-filled hard capsule.
Liquid-filled hard capsules are prepared by dissolving or dispersing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in suitable oils or lipid-based excipients to form a solution, suspension, or semi-solid, which is then filled into hollow hard capsules. Alternatively, a combination of oils, lipid excipients, and small units such as beads, mini-capsules, or micro-tablets can be co-filled into the capsule. After filling, the capsules are sealed using advanced banding or sealing technologies to close the gap between the capsule body and cap. Compared to traditional oral solid forms, liquid-filled hard capsules offer more versatile filling options.

To ensure quality and manufacturability, traditional oral solid forms often require the addition of numerous excipients. In contrast, liquid-filled hard capsules involve minimal use of chemically synthesized excipients commonly found in other oral forms. Furthermore, unlike soft capsules, they do not require large amounts of lubricants, minimizing the risk of equipment and product contamination and reducing the need for frequent cleaning — making the process safer and cleaner.
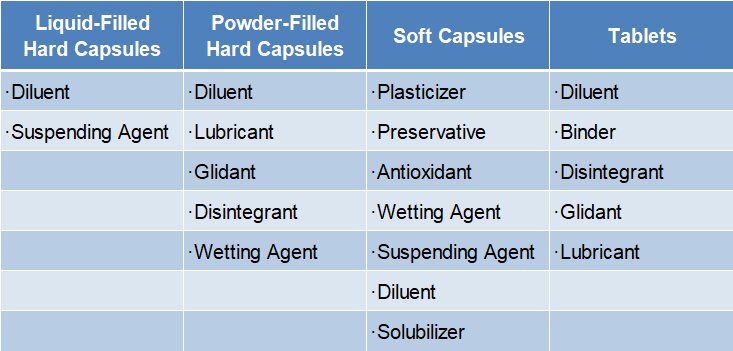
Traditional solid forms like tablets and powder-filled capsules must first dissolve before being absorbed by the body. Liquid-filled hard capsules deliver the drug in a pre-dissolved or suspended form, allowing for faster action and better protection against degradation in the stomach. This is especially beneficial for poorly water-soluble drugs, significantly enhancing their bioavailability. Additionally, the capsule shell of a liquid-filled hard capsule is about 0.1 mm thick, much thinner than the 0.7–0.9 mm thickness of soft capsules, making it easier to disintegrate and aiding faster absorption.
①Compared to soft capsules, hard capsule shells have lower moisture content and oxygen permeability, which helps in better microbial control.
②They are free from plasticizers, resulting in low migration rates and reduced risk of cross-linking reactions that could otherwise cause hardening or brittleness during storage, thus enhancing stability.
③The use of sealing bands not only prevents leakage but also significantly reduces the risks of oxidation, moisture uptake, and ingredient diffusion. Additionally, the seal acts as a tamper-evident feature, providing enhanced security against ingredient substitution.

Driven by advancements in formulation techniques and equipment development, liquid-filled hard capsules offer a valuable addition to the range of solid dosage forms. Their simple and safe composition minimizes the use of synthetic chemicals, preservatives, plasticizers, and disintegrants, thereby reducing the metabolic burden on the human body and improving bioavailability and product stability. In manufacturing, they provide advantages of simpler processes, accurate dosing, shorter production cycles, and lower operational costs.
Liquid-filled hard capsules represent a significant advancement in drug delivery technology. With ongoing innovations in pharmaceutical science, we can expect liquid-filled hard capsules to play an increasingly important role in the future of healthcare.

Customer Support: If you have any questions or need assistance, please contact our customer service team info@nutrigent.us. Our service hours are Monday to Friday, 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM.
DISCLAIMER: *These statements and any claims made about specific products on or through this site have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. This site is not intended to provide diagnosis, treatment, or medical advice, and all content provided is for informational purposes only.*